Adaptive AI

Welcome To the Arcade.
Dynamic Difficulty: Similar to the AI Director in Left 4 Dead, games like Alien: Isolation” use AI to adjust the game’s difficulty based on player performance. In “Alien: Isolation,” the Xenomorph’s behavior changes based on how the player interacts with the environment, making it more or less aggressive as needed to maintain tension.
Learning from Player Actions: Some horror games employ AI that learns from the player’s tactics. For example, in F.E.A.R., the AI-controlled enemies adapt their strategies, such as flanking or using cover, based on how players engage them, making each encounter feel unique.


Enemy Behavior
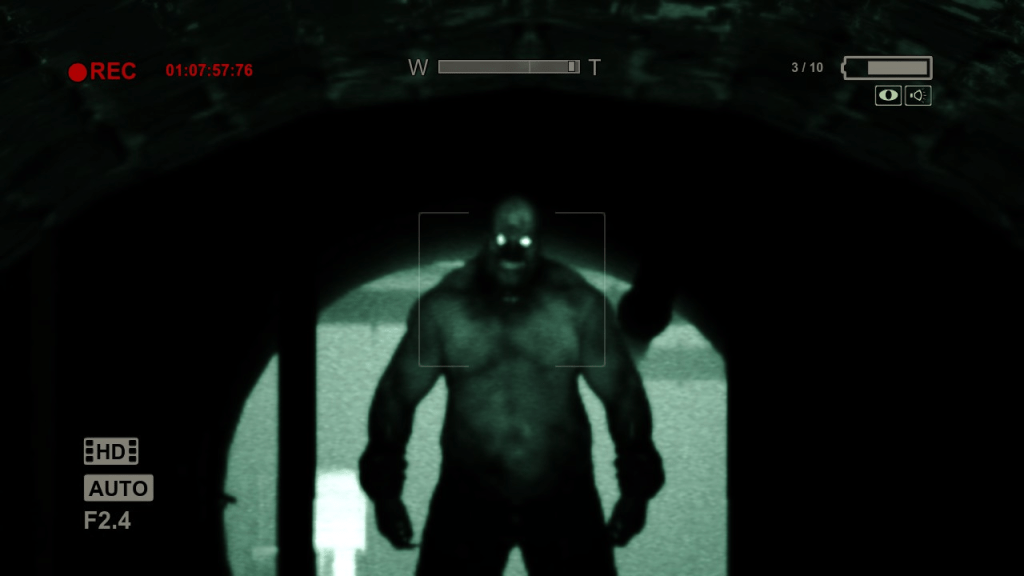
Unpredictable and Intelligent Enemies: Games like “Amnesia: The Dark Descent” feature enemies that react to light, sound, and player visibility, creating a cat-and-mouse gameplay experience where hiding and stealth are paramount. The AI in these games can make the enemy’s movements unpredictable, enhancing the horror.
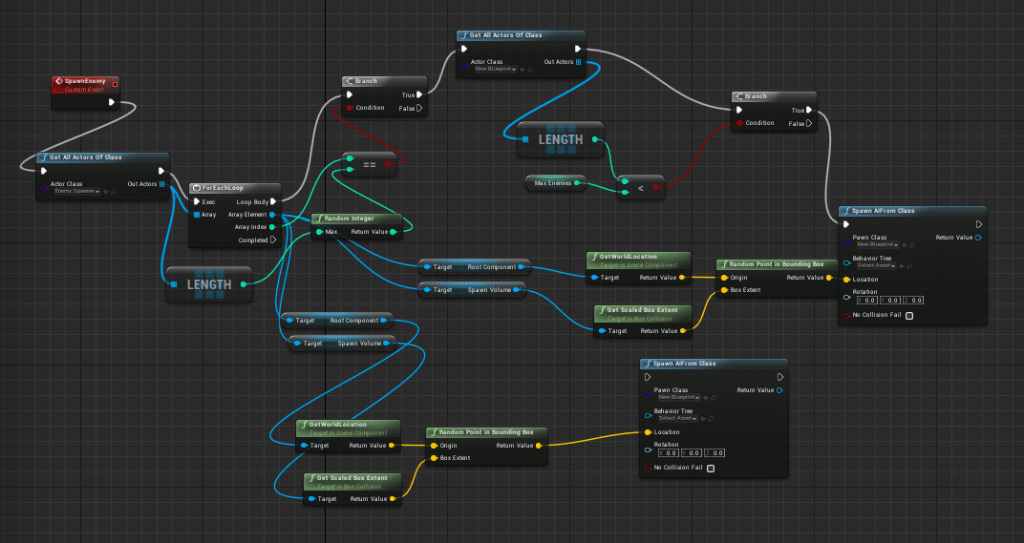
Dynamic Pathfinding: AI allows for complex pathfinding where enemies navigate environments in ways that feel natural and terrifying. In “Outlast,” the AI-controlled enemies chase players through complex environments, making escapes tense and unpredictable.
Atmosphere and Tension
Environmental Interaction: AI can control elements like sounds, lighting, and other environmental factors to build suspense. Games might use AI to subtly alter the game world around the player, like changing the weather or making objects move autonomously to suggest a presence.
Audio Cues: AI can manipulate audio in real-time, adjusting the intensity or direction of sounds to mislead or scare the player, contributing to psychological horror.

Storytelling and Narrative
Procedural Storytelling: AI can generate or alter narrative elements based on player actions. While not common, games like “SOMA” by Frictional Games use AI to adapt dialogues or events, making the story feel more personal and reactive to player decisions.

Character Behavior: NPCs in horror games can have AI-driven behaviors that make them react in more human-like ways, adding depth to the story or increasing the horror by making their reactions to the player’s presence or actions seem genuine.
Player Psychology
Psychological Profiling: Some horror games use AI to analyze player behavior to tailor the horror experience. This might involve ramping up jump scares if the player shows signs of being less affected or changing the type of horror elements introduced based on what seems to unnerve the player most.

Sensory Overload or Deprivation: AI can be used to manipulate sensory input, like in games where sudden changes in light or sound are used to disorient or scare the player.
Examples of AI in Horror Games:
Alien: Isolation – The Xenomorph’s AI is perhaps one of the most famous examples, creating a relentless, intelligent predator that learns from the player.
F.E.A.R. – Features some of the best squad AI in gaming, where enemies use tactics and cover effectively.
Outlast – Employs AI to control enemy behavior, making them react to noise and light, enhancing the survival horror experience.
Resident Evil 7: Biohazard – Uses AI to control enemies and manage encounters, making them feel more unpredictable and terrifying.
AI in horror games not only enhances gameplay mechanics but also plays a crucial role in crafting a deeply immersive and personal horror experience, where the game reacts to the player, turning each playthrough into a unique journey of terror. It’s very interesting if Ai can become a dungeon master of itself bringing endless jump scares and wicked scenarios in our very own game to enjoy like the first time around.

Leave a comment